Prescribed internal velocity constraints#
This section was contributed by Jonathan Perry-Houts
In cases where it is desirable to investigate the behavior of one part of the model domain but the controlling physics of another part is difficult to capture, such as corner flow in subduction zones, it may be useful to force the desired behavior in some parts of the model domain and solve for the resulting flow everywhere else. This is possible through the use of ASPECT’s “signal” mechanism, as documented in Extending ASPECT through signals.
Internally, adds “constraints” to the finite element system for boundary conditions and hanging nodes. These are places in the finite element system where certain solution variables are required to match some prescribed value. Although it is somewhat mathematically inadmissible to prescribe constraints on nodes inside the model domain, \(\Omega\), it is nevertheless possible so long as the prescribed velocity field fits in to the finite element’s solution space, and satisfies the other constraints (i.e., is divergence free).
Using ASPECT’s signals mechanism, we write a shared library which provides a “slot” that listens for the signal which is triggered after the regular model constraints are set, but before they are “distributed”;
As an example of this functionality, below is a plugin which allows the user to prescribe internal velocities with functions in a parameter file:
/*
Copyright (C) 2011 - 2022 by the authors of the ASPECT code.
This file is part of ASPECT.
ASPECT is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation; either version 2, or (at your option)
any later version.
ASPECT is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with ASPECT; see the file LICENSE. If not see
<http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
#include <deal.II/base/parameter_handler.h>
#include <deal.II/base/parsed_function.h>
#include <deal.II/fe/fe_values.h>
#include <aspect/global.h>
#include <aspect/utilities.h>
#include <aspect/simulator_signals.h>
#include <aspect/parameters.h>
namespace aspect
{
using namespace dealii;
// Global variables (to be set by parameters)
bool prescribe_internal_velocities;
// Because we do not initially know what dimension we're in, we need
// function parser objects for both 2d and 3d.
Functions::ParsedFunction<2> prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_2d (2);
Functions::ParsedFunction<3> prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_3d (3);
Functions::ParsedFunction<2> prescribed_velocity_function_2d (2);
Functions::ParsedFunction<3> prescribed_velocity_function_3d (3);
/**
* Declare additional parameters.
*/
void declare_parameters(const unsigned int dim,
ParameterHandler &prm)
{
prm.declare_entry ("Prescribe internal velocities", "false",
Patterns::Bool (),
"Whether or not to use any prescribed internal velocities. "
"Locations in which to prescribe velocities are defined "
"in section ``Prescribed velocities/Indicator function'' "
"and the velocities are defined in section ``Prescribed "
"velocities/Velocity function''. Indicators are evaluated "
"at the center of each cell, and all DOFs associated with "
"the specified velocity component at the indicated cells "
"are constrained."
);
prm.enter_subsection ("Prescribed velocities");
{
prm.enter_subsection ("Indicator function");
{
if (dim == 2)
Functions::ParsedFunction<2>::declare_parameters (prm, 2);
else
Functions::ParsedFunction<3>::declare_parameters (prm, 3);
}
prm.leave_subsection ();
prm.enter_subsection ("Velocity function");
{
if (dim == 2)
Functions::ParsedFunction<2>::declare_parameters (prm, 2);
else
Functions::ParsedFunction<3>::declare_parameters (prm, 3);
}
prm.leave_subsection ();
}
prm.leave_subsection ();
}
template <int dim>
void parse_parameters(const Parameters<dim> &,
ParameterHandler &prm)
{
prescribe_internal_velocities = prm.get_bool ("Prescribe internal velocities");
prm.enter_subsection ("Prescribed velocities");
{
prm.enter_subsection("Indicator function");
{
try
{
if (dim == 2)
prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_2d.parse_parameters (prm);
else
prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_3d.parse_parameters (prm);
}
catch (...)
{
std::cerr << "ERROR: FunctionParser failed to parse\n"
<< "\t'Prescribed velocities.Indicator function'\n"
<< "with expression\n"
<< "\t'" << prm.get("Function expression") << "'";
throw;
}
}
prm.leave_subsection();
prm.enter_subsection("Velocity function");
{
try
{
if (dim == 2)
prescribed_velocity_function_2d.parse_parameters (prm);
else
prescribed_velocity_function_3d.parse_parameters (prm);
}
catch (...)
{
std::cerr << "ERROR: FunctionParser failed to parse\n"
<< "\t'Prescribed velocities.Velocity function'\n"
<< "with expression\n"
<< "\t'" << prm.get("Function expression") << "'";
throw;
}
}
prm.leave_subsection();
}
prm.leave_subsection ();
}
/**
* A set of helper functions that either return the point passed to it (if
* the current dimension is the same) or return a dummy value (otherwise).
*/
namespace
{
const Point<2> as_2d(const Point<3> &/*p*/)
{
return Point<2>();
}
const Point<2> &as_2d(const Point<2> &p)
{
return p;
}
const Point<3> as_3d(const Point<2> &/*p*/)
{
return Point<3>();
}
const Point<3> &as_3d(const Point<3> &p)
{
return p;
}
}
/**
* This function is called by a signal which is triggered after the other constraints
* have been calculated. This enables us to define additional constraints in the mass
* matrix on any arbitrary degree of freedom in the model space.
*/
template <int dim>
void constrain_internal_velocities (const SimulatorAccess<dim> &simulator_access,
AffineConstraints<double> ¤t_constraints)
{
if (prescribe_internal_velocities)
{
const Parameters<dim> ¶meters = simulator_access.get_parameters();
const std::vector<Point<dim>> points = aspect::Utilities::get_unit_support_points(simulator_access);
const Quadrature<dim> quadrature (points);
FEValues<dim> fe_values (simulator_access.get_fe(), quadrature, update_quadrature_points);
typename DoFHandler<dim>::active_cell_iterator cell;
// Loop over all cells
for (cell = simulator_access.get_dof_handler().begin_active();
cell != simulator_access.get_dof_handler().end();
++cell)
if (! cell->is_artificial())
{
fe_values.reinit (cell);
std::vector<types::global_dof_index> local_dof_indices(simulator_access.get_fe().dofs_per_cell);
cell->get_dof_indices (local_dof_indices);
for (unsigned int q=0; q<quadrature.size(); q++)
// If it's okay to constrain this DOF
if (current_constraints.can_store_line(local_dof_indices[q]) &&
!current_constraints.is_constrained(local_dof_indices[q]))
{
// Get the velocity component index
const unsigned int c_idx =
simulator_access.get_fe().system_to_component_index(q).first;
// If we're on one of the velocity DOFs
if ((c_idx >=
simulator_access.introspection().component_indices.velocities[0])
&&
(c_idx <=
simulator_access.introspection().component_indices.velocities[dim-1]))
{
// Which velocity component is this DOF associated with?
const unsigned int component_direction
= (c_idx
- simulator_access.introspection().component_indices.velocities[0]);
// we get time passed as seconds (always) but may want
// to reinterpret it in years
double time = simulator_access.get_time();
if (simulator_access.convert_output_to_years())
time /= year_in_seconds;
prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_2d.set_time (time);
prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_3d.set_time (time);
prescribed_velocity_function_2d.set_time (time);
prescribed_velocity_function_3d.set_time (time);
const Point<dim> p = fe_values.quadrature_point(q);
// Because we defined and parsed our parameter
// file differently for 2d and 3d we need to
// be sure to query the correct object for
// function values. The function parser
// objects expect points of a certain
// dimension, but Point p will be compiled for
// both 2d and 3d, so we need to do some trickery
// to make this compile.
double indicator, u_i;
if (dim == 2)
{
indicator = prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_2d.value
(as_2d(p),
component_direction);
u_i = prescribed_velocity_function_2d.value
(as_2d(p),
component_direction);
}
else
{
indicator = prescribed_velocity_indicator_function_3d.value
(as_3d(p),
component_direction);
u_i = prescribed_velocity_function_3d.value
(as_3d(p),
component_direction);
}
if (indicator > 0.5)
{
// Add a constraint of the form dof[q] = u_i
// to the list of constraints.
current_constraints.add_line (local_dof_indices[q]);
// When using a defect correction solver, the constraints should only be set on
// nonlinear iteration 0.
if (
(parameters.nonlinear_solver!=Parameters<dim>::NonlinearSolver::no_Advection_iterated_defect_correction_Stokes &&
parameters.nonlinear_solver!=Parameters<dim>::NonlinearSolver::single_Advection_iterated_defect_correction_Stokes &&
parameters.nonlinear_solver!=Parameters<dim>::NonlinearSolver::iterated_Advection_and_defect_correction_Stokes &&
parameters.nonlinear_solver!=Parameters<dim>::NonlinearSolver::iterated_Advection_and_Newton_Stokes &&
parameters.nonlinear_solver!=Parameters<dim>::NonlinearSolver::single_Advection_iterated_Newton_Stokes ) ||
simulator_access.get_nonlinear_iteration() == 0
)
{
current_constraints.set_inhomogeneity (local_dof_indices[q], u_i);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Connect declare_parameters and parse_parameters to appropriate signals.
void parameter_connector ()
{
SimulatorSignals<2>::declare_additional_parameters.connect (&declare_parameters);
SimulatorSignals<3>::declare_additional_parameters.connect (&declare_parameters);
SimulatorSignals<2>::parse_additional_parameters.connect (&parse_parameters<2>);
SimulatorSignals<3>::parse_additional_parameters.connect (&parse_parameters<3>);
}
// Connect constraints function to correct signal.
template <int dim>
void signal_connector (SimulatorSignals<dim> &signals)
{
signals.post_constraints_creation.connect (&constrain_internal_velocities<dim>);
}
// Tell ASPECT to send signals to the connector functions
ASPECT_REGISTER_SIGNALS_PARAMETER_CONNECTOR(parameter_connector)
ASPECT_REGISTER_SIGNALS_CONNECTOR(signal_connector<2>, signal_connector<3>)
}
The above plugin can be compiled with cmake . && make in the
cookbooks/prescribed_velocity directory. It can be loaded in a parameter
file as an “Additional shared library” By setting parameters like
those shown below, it is possible to produce many interesting flow fields such
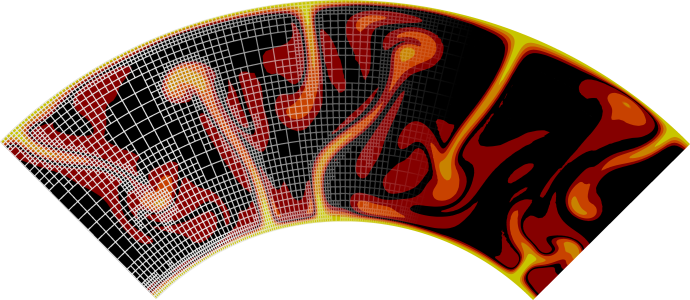
as the ones visualized in Fig. 60.
## First we set up a unit length box model with uniform everything.
set Dimension = 2
set End time = 0
# Load the signal library.
set Additional shared libraries = ./libprescribed_velocity.so
set Output directory = output-corner_flow
## Turn prescribed velocities on
set Prescribe internal velocities = true
subsection Geometry model
set Model name = box
end
subsection Initial temperature model
set Model name = function
end
subsection Boundary velocity model
set Zero velocity boundary indicators = top
end
subsection Gravity model
set Model name = vertical
subsection Vertical
set Magnitude = 0
end
end
subsection Material model
set Model name = simple
end
subsection Mesh refinement
set Initial global refinement = 7
set Initial adaptive refinement = 0
end
subsection Postprocess
set List of postprocessors = visualization
end
subsection Prescribed velocities
subsection Indicator function
set Variable names = x,y,t
# Return where to prescribe u_x; u_y; u_z
# (last one only used if dimension = 3)
# 1 if velocity should be prescribed, 0 otherwise
set Function expression = if(((x>.1)&(x<.9))&(abs(x-(1-y))<.01),1,0); \
if(((x>.1)&(x<.9))&(abs(x-(1-y))<.01),1,0)
end
subsection Velocity function
set Variable names = x,y,t
# Return u_x; u_y; u_z (u_z only used if in 3d)
set Function expression = 1;-1
end
end
Fig. 60 Examples of flows with prescribed internal velocities.#